Selenium Derivatives
- Methyl Iodide
- Ethyl Iodide
- n-Butyl Iodide
- N-propyl Iodide
- 2-Ethylhexyl Iodide
- Diiodomethane
- Chloroiodomethane
- 5-Iodo-2-methylbenzoic Acid
- 2-chloro-5-iodobenzoic acid
- Methyl-2-Iodobenzoate
- 2-Iodobenzoic Acid
- 3,5-Diiodosalicylic Acid
- N-Iodosuccinimide
- Tetrabutylammonium Iodide
- Iodine Monochloride
- 5-Iodoanthranilic acid
- Iodoform
- Potassium iodide
- Sodium Iodide
- Ammonium Iodide
- Cuprous Iodide
- Zinc Iodide
- Sodium Metaperiodate
- Potassium Iodate
- Calcium Iodate
- Iodic acid
- Periodic acid
- Hydriodic Acid
- Iodobenzene Diacetate
- Dess Martin Periodinane
- 1,4-Diiodobenzene
- 4-Bromoiodobenzene
- 4-Chloroiodobenzene
- Iodobenzene
- 4-Iodoaniline
- 4-Iodotoluene
- 4-Iodoanisole
- 4-Iodophenol
- 4,4'-Diiodobiphenyl
- Trimethylsulfoxonium Iodide
Cuprous Iodide
Cuprous Iodide ( Copper (I) iodide ) is the chemical compound with the formula CuI; it is also known as cuprous iodide. Copper (I) iodide is useful in a variety of applications ranging from organic synthesis to cloud seeding.
Copper (I) iodide is white, but samples are often tan or even, when found in nature as rare mineral marshite, reddish brown, but such color is due to impurities.
It is common for iodides to become discolored because of the easy oxidation of the iodide anion to iodine. Copper (I) iodide can also be prepared by heating iodine and copper in concentrated hydriodic acid, HI.
| Product | Cuprous Iodide (Copper (I) Iodide) |
| Structural formula | 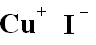 |
| CAS No. | [7681-65-4] |
| Molecular formula | CuI |
| Molecular weight | 190.45 |
| Description | Off white to light brown powder. |
| Loss on drying | Max. 0.50 % |
| Assay | Min. 99.0% |